Oligopeptides containing 'EWS' motif are good candidates for study of chemotactic behaviour of ligands (Kõhidai et al., Cell Biochem. Funct. 21: 113, 2003)
Significance of these sequences is great in biology and especially in immune responses as they are expressed in the extracellular WSXWS domains of a cytikine superfamily, including IL-2, IL-4 and IL-6 receptors. Induction of haptotaxis is conceivable by the membrane bound EWS ligands, while they can also possess classical chemoattractant moiety via soluble receptors.
Investigation of 3-7-mer peptides (EWS-SEWS-WSEWS-EWSEWS-GEWSEWS) and their peptide amides shows that slight differences in sequence or chemical structure e.g. amidation results significant differences in chemoattractant properties of the ligands, even at relatively low concentrations (SEWS 10-12M).
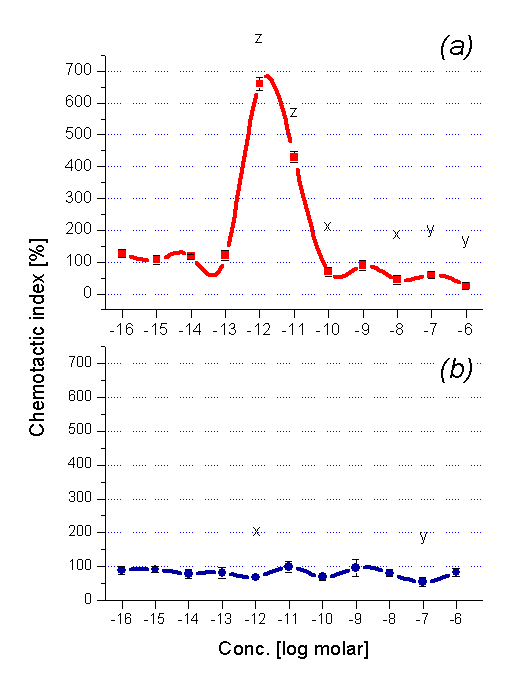
SEWE-OH proved to possess an extraordinally strong (a -SEWS-OH 660%) chemoattractant ability. Amidation of the C-terminus of the peptide (b - SEWS-NH2) results the complete loss of the chemoattractant moiety. In some derivatives amidation has opposite, enhancer effect e.g. EWS-NH2.